как установить докер linux
Установка Docker на Linux
Мы рассмотрим процесс установки Docker на системы семейства Linux — а именно, CentOS, Fedora и Ubuntu.
Ubuntu
Docker на Ubuntu ставится, относительно, просто.
Обновляем список пакетов:
Устанавливаем докер командой:
apt-get install docker docker.io
Разрешаем автозапуск докера и стартуем его:
systemctl enable docker
systemctl start docker
CentOS 8
Скачиваем конфигурационный файл для репозитория докер:
Теперь устанавливаем docker:
dnf install docker-ce docker-ce-cli
И разрешаем автозапуск сервиса и стартуем его:
CentOS 7
Скачиваем файл репозитория:
yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
Запускаем его и разрешаем автозапуск:
Fedora
Устанавливаем плагин, дающий дополнительные инструменты при работе с пакетами:
yum install dnf-plugins-core
dnf install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
Запускаем его и разрешаем автозапуск:
Проверка
Чтобы убедиться, что docker в рабочем состоянии, выполняем команду:
docker run hello-world
Сначала система обнаружит, что нужного образа нет и загрузит его:
Unable to find image ‘hello-world:latest’ locally
latest: Pulling from library/hello-world
b8dfde127a29: Already exists
Digest: sha256:308866a43596e83578c7dfa15e27a73011bdd402185a84c5cd7f32a88b501a24
Status: Downloaded newer image for hello-world:latest
После отобразит приветствие:
Hello from Docker!
This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.
To generate this message, Docker.
Docker работает корректно.
Установка Compose
Команда docker-compose позволяет развернуть многоконтейнерные Docker-приложения.
Для ее установка сначала переходим на страницу github.com/docker/compose/releases/latest и смотрим последнюю версию docker-compose. В моем случае, это была 1.29.2.
* где 1.29.2 — последняя версия файла.
Даем права файлу на исполнение:
chmod +x /usr/bin/docker-compose
Запускаем docker-compose с выводом его версии:
Возможные проблемы
1. undefined symbol: seccomp_api_set
Сервис докера не запускается, а в логе можно увидеть следующий текст ошибки:
/usr/bin/containerd: symbol lookup error: /usr/bin/containerd: undefined symbol: seccomp_api_set
Причина: ошибка возникает, если установить свежую версию containerd на систему с необновленной библиотекой libseccomp.
Решение: обновляем libseccomp.
yum update libseccomp
2. error initializing network controller list bridge addresses failed no available network
Сервис докера не запускается, а в логе можно увидеть следующий текст ошибки:
error initializing network controller list bridge addresses failed no available network
Причина: система не может создать docker-интерфейс.
Решение: создаем docker-интерфейс вручную. Устанавливаем утилиту для работы с bridge-интерфейсами.
yum install bridge-utils
apt-get install bridge-utils
brctl addbr docker0
Назначаем IP-адреса на созданный интерфейс:
ip addr add 192.168.84.1/24 dev docker0
* в нашем примере для docker мы задали адрес 192.168.84.1.
Install Docker Engine
Estimated reading time: 7 minutes
Docker Desktop for Linux
Docker Desktop helps you build, share, and run containers easily on Mac and Windows as you do on Linux. Docker handles the complex setup and allows you to focus on writing the code. Thanks to the positive support we received on the subscription updates, we’ve started working on Docker Desktop for Linux which is the second-most popular feature request in our public roadmap. If you are interested in early access, sign up for our Developer Preview program.
Supported platforms
Docker Engine is available on a variety of Linux platforms, macOS and Windows 10 through Docker Desktop, and as a static binary installation. Find your preferred operating system below.
Desktop
Server
| Platform | x86_64 / amd64 | arm64 / aarch64 | arm (32-bit) | s390x |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CentOS |  |  | В | В |
| Debian |  |  |  | В |
| Fedora |  |  | В | В |
| Raspbian | В | В |  | В |
| RHEL | В | В | В |  |
| SLES | В | В | В |  |
| Ubuntu |  |  |  |  |
| Binaries |  |  |  | В |
Other Linux distributions
While the instructions below may work, Docker does not test or verify installation on derivatives.
Docker provides binaries for manual installation of Docker Engine. These binaries are statically linked and can be used on any Linux distribution.
Release channels
Docker Engine has three types of update channels, stable, test, and nightly:
Stable
In preparation for a new year-month release, a branch is created from the master branch with format YY.mm when the milestones desired by Docker for the release have achieved feature-complete. Pre-releases such as betas and release candidates are conducted from their respective release branches. Patch releases and the corresponding pre-releases are performed from within the corresponding release branch.
Nightly
Nightly builds give you the latest builds of work in progress for the next major release. They are created once per day from the master branch with the version format:
These builds allow for testing from the latest code on the master branch. No qualifications or guarantees are made for the nightly builds.
Support
Docker Engine releases of a year-month branch are supported with patches as needed for one month after the next year-month general availability release.
This means bug reports and backports to release branches are assessed until the end-of-life date.
After the year-month branch has reached end-of-life, the branch may be deleted from the repository.
Backporting
Backports to the Docker products are prioritized by the Docker company. A Docker employee or repository maintainer will endeavour to ensure sensible bugfixes make it into active releases.
If there are important fixes that ought to be considered for backport to active release branches, be sure to highlight this in the PR description or by adding a comment to the PR.
Upgrade path
Patch releases are always backward compatible with its year-month version.
Licensing
Docker is licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0. See LICENSE for the full license text.
Reporting security issues
The Docker maintainers take security seriously. If you discover a security issue, please bring it to their attention right away!
Please DO NOT file a public issue; instead send your report privately to security@docker.com.
Security reports are greatly appreciated, and Docker will publicly thank you for it.
Get started
After setting up Docker, you can learn the basics with Getting started with Docker.
Install Docker Engine on Ubuntu
Estimated reading time: 11 minutes
Docker Desktop for Linux
Docker Desktop helps you build, share, and run containers easily on Mac and Windows as you do on Linux. Docker handles the complex setup and allows you to focus on writing the code. Thanks to the positive support we received on the subscription updates, we’ve started working on Docker Desktop for Linux which is the second-most popular feature request in our public roadmap. If you are interested in early access, sign up for our Developer Preview program.
To get started with Docker Engine on Ubuntu, make sure you meet the prerequisites, then install Docker.
Prerequisites
OS requirements
To install Docker Engine, you need the 64-bit version of one of these Ubuntu versions:
Ubuntu 16.04 LTS “Xenial Xerus” end-of-life
Ubuntu Linux 16.04 LTS reached the end of its five-year LTS window on April 30th 2021 and is no longer supported. Docker no longer releases packages for this distribution (including patch- and security releases). Users running Docker on Ubuntu 16.04 are recommended to update their system to a currently supported LTS version of Ubuntu.
Uninstall old versions
It’s OK if apt-get reports that none of these packages are installed.
Supported storage drivers
Docker Engine uses the overlay2 storage driver by default. If you need to use aufs instead, you need to configure it manually. See use the AUFS storage driver
Installation methods
You can install Docker Engine in different ways, depending on your needs:
Most users set up Docker’s repositories and install from them, for ease of installation and upgrade tasks. This is the recommended approach.
Some users download the DEB package and install it manually and manage upgrades completely manually. This is useful in situations such as installing Docker on air-gapped systems with no access to the internet.
In testing and development environments, some users choose to use automated convenience scripts to install Docker.
Install using the repository
Before you install Docker Engine for the first time on a new host machine, you need to set up the Docker repository. Afterward, you can install and update Docker from the repository.
Set up the repository
Update the apt package index and install packages to allow apt to use a repository over HTTPS:
Add Docker’s official GPG key:
Use the following command to set up the stable repository. To add the nightly or test repository, add the word nightly or test (or both) after the word stable in the commands below. Learn about nightly and test channels.
Install Docker Engine
Update the apt package index, and install the latest version of Docker Engine and containerd, or go to the next step to install a specific version:
Got multiple Docker repositories?
If you have multiple Docker repositories enabled, installing or updating without specifying a version in the apt-get install or apt-get update command always installs the highest possible version, which may not be appropriate for your stability needs.
To install a specific version of Docker Engine, list the available versions in the repo, then select and install:
a. List the versions available in your repo:
b. Install a specific version using the version string from the second column, for example, 5:18.09.1
Verify that Docker Engine is installed correctly by running the hello-world image.
This command downloads a test image and runs it in a container. When the container runs, it prints a message and exits.
Docker Engine is installed and running. The docker group is created but no users are added to it. You need to use sudo to run Docker commands. Continue to Linux postinstall to allow non-privileged users to run Docker commands and for other optional configuration steps.
Upgrade Docker Engine
Install from a package
Install Docker Engine, changing the path below to the path where you downloaded the Docker package.
The Docker daemon starts automatically.
Verify that Docker Engine is installed correctly by running the hello-world image.
This command downloads a test image and runs it in a container. When the container runs, it prints a message and exits.
Docker Engine is installed and running. The docker group is created but no users are added to it. You need to use sudo to run Docker commands. Continue to Post-installation steps for Linux to allow non-privileged users to run Docker commands and for other optional configuration steps.
Upgrade Docker Engine
To upgrade Docker Engine, download the newer package file and repeat the installation procedure, pointing to the new file.
Install using the convenience script
Docker provides a convenience script at get.docker.com to install Docker into development environments quickly and non-interactively. The convenience script is not recommended for production environments, but can be used as an example to create a provisioning script that is tailored to your needs. Also refer to the install using the repository steps to learn about installation steps to install using the package repository. The source code for the script is open source, and can be found in the docker-install repository on GitHub.
Always examine scripts downloaded from the internet before running them locally. Before installing, make yourself familiar with potential risks and limitations of the convenience script:
Tip: preview script steps before running
You can run the script with the DRY_RUN=1 option to learn what steps the script will execute during installation:
This example downloads the script from get.docker.com and runs it to install the latest stable release of Docker on Linux:
Docker is installed. The docker service starts automatically on Debian based distributions. On RPM based distributions, such as CentOS, Fedora, RHEL or SLES, you need to start it manually using the appropriate systemctl or service command. As the message indicates, non-root users cannot run Docker commands by default.
Use Docker as a non-privileged user, or install in rootless mode?
The installation script requires root or sudo privileges to install and use Docker. If you want to grant non-root users access to Docker, refer to the post-installation steps for Linux. Docker can also be installed without root privileges, or configured to run in rootless mode. For instructions on running Docker in rootless mode, refer to run the Docker daemon as a non-root user (rootless mode).
Install pre-releases
To install the latest version of Docker on Linux from the “test” channel, run:
Upgrade Docker after using the convenience script
If you installed Docker using the convenience script, you should upgrade Docker using your package manager directly. There is no advantage to re-running the convenience script, and it can cause issues if it attempts to re-add repositories which have already been added to the host machine.
Uninstall Docker Engine
Uninstall the Docker Engine, CLI, and Containerd packages:
Images, containers, volumes, or customized configuration files on your host are not automatically removed. To delete all images, containers, and volumes:
You must delete any edited configuration files manually.
Как установить Docker на Linux Mint 20
Как установить Docker на Linux Mint 20
В этом руководстве мы покажем вам, как установить Docker на Linux Mint 20. Для тех из вас, кто не знал, Docker — это проект с открытым исходным кодом, который автоматизирует развертывание приложения внутри программного контейнера. Контейнер позволяет разработчику упаковать все ресурсы проекта, такие как библиотеки, зависимости, активы и т. Д. Docker написан на языке программирования Go и разработан Dot cloud. По сути, это механизм контейнеров, который использует функции ядра Linux, такие как пространства имен и группы управления, для создания контейнеров поверх операционной системы и автоматизирует развертывание приложений в контейнере.
В этой статье предполагается, что у вас есть хотя бы базовые знания Linux, вы знаете, как использовать оболочку, и, что наиболее важно, вы размещаете свой сайт на собственном VPS. Установка довольно проста и предполагает, что вы работаете с учетной записью root, в противном случае вам может потребоваться добавить ‘ sudo ‘ к командам для получения привилегий root. Я покажу вам пошаговую установку Docker на Linux Mint 20 (Ульяна).
Установить Docker на Linux Mint 20 Ulyana
Шаг 1. Перед запуском приведенного ниже руководства важно убедиться, что ваша система обновлена, выполнив следующие apt команды в терминале:
Шаг 2. Установка Docker на Linux Mint 20.
Выполните следующую команду, чтобы установить пакеты Snap и Docker:
Чтобы установить Docker, просто используйте следующую команду:
Теперь мы добавляем официальный ключ Docker в вашу систему Linux Mint:
Шаг 3. Затем добавьте репозиторий Docker в Linux Mint:
Шаг 4. Затем установите Docker CE с помощью следующей команды:
После установки будет создана группа докеров. Добавьте своего пользователя в группу, которая будет запускать команды докеров:
После этого проверьте установку Docker, используя следующую команду:
Docker используется с синтаксисом, как показано ниже:
Как установить Docker на Linux сервер
Сейчас читают:
Содержание:
Основные понятия
Подробнее с экосистемой Docker можно ознакомиться в отдельной статье нашего блога.
Условия для запуска Docker на VPS-сервере с Linux
Подробнее о том, как работать с контейнером Docker можно прочитать в этой статье.
Процессы установки и работы с докер-системой в Debian и Ubuntu фактически одинаковы — меняются только наименования версий ОС. Поэтому, сначала будет рассмотрена общая установка для этих версий, а потом — отдельная инструкция по Centos.
Установка Docker на Ubuntu и Debian
Развернуть окружение Docker на виртуальном сервере с Debian или Ubuntu можно из официального репозитория. Для этого необходимо произвести приведенную ниже последовательность действий.
В результате должен получиться вывод:
Примечание! При настройке под Ubuntu возврат будет с наименованиями, соответствующим текущей версии.
Теперь можно осуществить развертывание Docker на сервере.
Docker под Ubuntu или Debian будет установлен автоматически.
Команда должна вернуть следующее:
Работа с образами в Debian/Ubuntu
Для чего создаются образы и как работают контейнеры в Docker можно узнать в этой статье.
Далее будет разобран алгоритм действий для работы с образами в установленном Docker.
1. Для начала, нужно проверить возможность загрузки и установки образов из DockerHub командой:
Возврат должен быть соответствующего содержания:
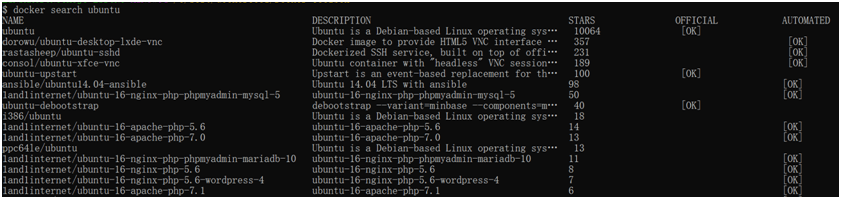
2. Для поиска готовых образов на DockerHub следует ввести команду Docker с подкомандой «search»:
Возврат выдаст реестр всех доступных образов Ubuntu в виде довольно обширного списка.
3. Команда «Pull» поможет загрузить нужный образ:
Как установить Docker на Centos
Процесс развертки Docker на сервере под Centos намного проще, чем два рассмотренных выше случая.
1. Произвести пакетное обновление сервера:
2. Ввести команду для установки платформы Docker:
3. Если требуется запустить docker от root, необходимо ввести следующую команду:
4. Ввести команду запуска Docker под Centos:
Работа с образами в Centos
Для работы с образами Docker на VPS под Centos необходимо вводить те же команды, что и в Debian/Ubuntu:
Начни экономить на хостинге сейчас — 14 дней бесплатно!