windows web deploy что это
Microsoft Web Deploy что это за программа?


Это бесплатная программа, она не грузит никак комп, но если она вам не нужна то ей не место на вашем компе и лучше ее снести…
Вот что мне нравится в софте от Microsoft, даже если это какая-то мелкая утилита типа Microsoft Web Deploy, это то что их софт редко когда глючит. Это я к тому, что даже если вы не пользуетесь прогой и она у вас просто сидит в списке, то она никак не грузит комп вообще! Вот сейчас у меня Windows 10 и я сам себе не могу поверить но я …перестал заниматься всякой оптимизацией! Я ничего не отключаю теперь, я провел куча тестов и понял что ничего тут не нужно делать. Все что делается в винде в фоновом режиме, все это не особо тормозит комп и не отнимает ресурсы. Вот сами проверьте, установите Windows 10, обновите ее, и оставьте в покое. И вы сами убедитесь что она загружает процессор ровно на 0%…
Кстати я слушаю музыку в Хроме, а если быть точнее то на Ютубе, так в таком режиме Хром у меня потребляет около 0-1%… вот такие дела.. Я сам удивлен, Ютуб это же все такие медиа контент, а тормозов нет вообще (как я понимаю это все таки из-за браузера Хром, ибо в Мозилле Ютуб все таки немного грузит проц).
Мораль сей басни какова? Если вы видите какую-то прогу, которая от Microsoft, ну например Microsoft Web Deploy, то если вы не знаете что это такое то и не нужно удалять! Проблем набраться можно легко, а вот исправить…
Но с Microsoft Web Deploy все проще, это можно удалить и ничего винде не будет, все будет работать и дальше нормуль
У вас скорее всего установлена данная программа будет в папке IIS:
При этом внутри будут две папки Microsoft Web Deploy:
Там где просто папка, без приставки V3, то там внутри просто библиотека Microsoft.Web.Deployment.dll, а вот в папке Microsoft Web Deploy V3 будет куча всего:
Как видите тут все засекречено ничего не понятно…
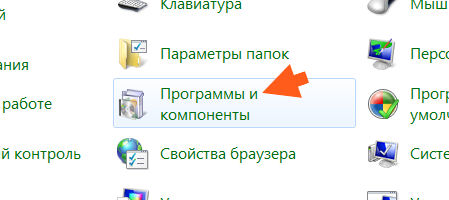
Итак, чтобы удалить программу Microsoft Web Deploy, вам нужно открыть меню Пуск и там нажать на Панель управления:
Если у вас Windows 10, то там данный пункт находится в меню, которое вызывается кнопками Win + X!
Потом в открытом окне находим и запускаем значок Программы и компоненты:
Находим там Microsoft Web Deploy 3.0 (у вас может быть другая версия), нажимаем правой кнопкой и выбираем Удалить:
Выскочит такое сообщение, нажимаете тут Да:
Оно пройдет быстро, после чего программы уже не будет в списке! Как видите ничего сложного. Я лично потом сделал перезагрузку и проверил, все работает нормально и никаких косяков мной замечено не было.
На этом все, надеюсь что данная инфа была вам полезной. Желаю вам удачи
Добавить комментарий Отменить ответ
Этот сайт использует Akismet для борьбы со спамом. Узнайте как обрабатываются ваши данные комментариев.
Introduction to Web Deploy
What is Web Deploy?
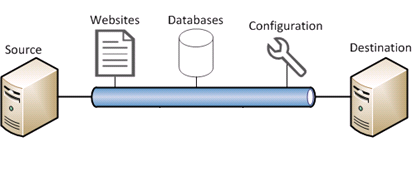
Web Deploy is an extensible client-server tool for syncing content and configuration to IIS. Web Deploy is used primarily in two scenarios:
How does Web Deploy compare to FTP?
Web Deploy is often compared to technologies like FTP, XCOPY or RoboCopy. While these technologies are useful, Web Deploy offers several benefits.
Here is a comparison of Web Deploy to FTP:
How does it work?
Most of the Web Deploy operations are modeled around sync operation between a source and a destination. Sync operation is orchestrated by Web Deploy framework using one or more Web deploy providers as described below.
Framework
Web Deploy consists of a framework which manages connection state and orchestrates the sync between source & destination. For example, the framework is responsible for skipping syncing certain types of content, running rules and transforming files.
The framework is accessible via a public API as well as via a command-line executable, msdeploy.exe.
Providers
Web Deploy can synchronize any kind of data between two locations through the use of its built-in providers which plug into the framework. Providers know how to synchronize a particular type of data between two sources, or retrieve useful information about the data source.
For example, Web Deploy has a provider that works with SQL databases (dbFullSql) that can synchronize an entire SQL Server database to another server. Other built-in providers synchronize MySQL databases (dbMySql), IIS 7 configuration (appHostConfig), GAC assemblies (gacAssembly), or COM objects (comObject32/comObject64). A more complete listing can be found on TechNet.
The provider model is extensible and lets developers write their own providers for Web Deploy if they need to synchronize custom data.
Under the Hood
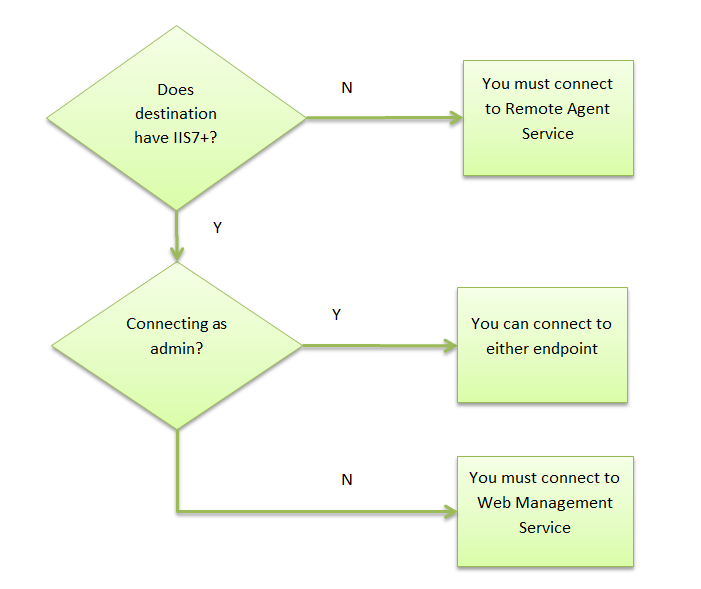
When a source initiates an action through Web Deploy, the Web Deploy Framework establishes a connection with the destination. Web Deploy supports two connection end-points, and the one you use depends on several factors:
Руководство по установке и настройке Web Deploy в среде Windows Server 2008 R2
Установка Web Deploy
Web Deploy можно установить двумя способами (мне именно так и пришлось).
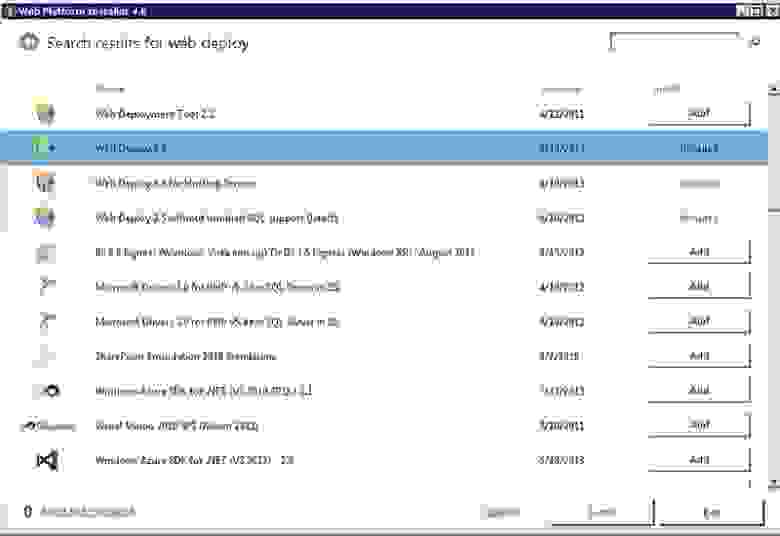
Web Platform Installer
Первый способ через Web Platform Installer. Его необходимо скачать и установить на сервер. Затем открыть и выбрать такие пункты как: Web Deploy, Web Deploy for Hosting Servers и IIS Recommendated Configuration (на скриншоте не видно)
Пакеты, устанавливаемые через WPI включают в себя дополнительные компоненты, некоторым может это не понравится. Однако для новчиков этот путь будет самый простой.
Установка через msi
Необходимо скачать файл установки Web Deploy (на сегодня версии 3.5) и установить его. При ручной установке необходимо будет вручную установить необходимые службы IIS. Делается это через панель управления сервером: Roles > IIS > Add Role Services
Настройка сайта для удаленной публикации
После всех дейсвий должен был появиться пункт меню
Создаем пользователя не администратора и задаем ему сложный пароль. Также даем ему права на запись в папку сайта в wwwroot.
Далее настраиваем удаленную публикацию:
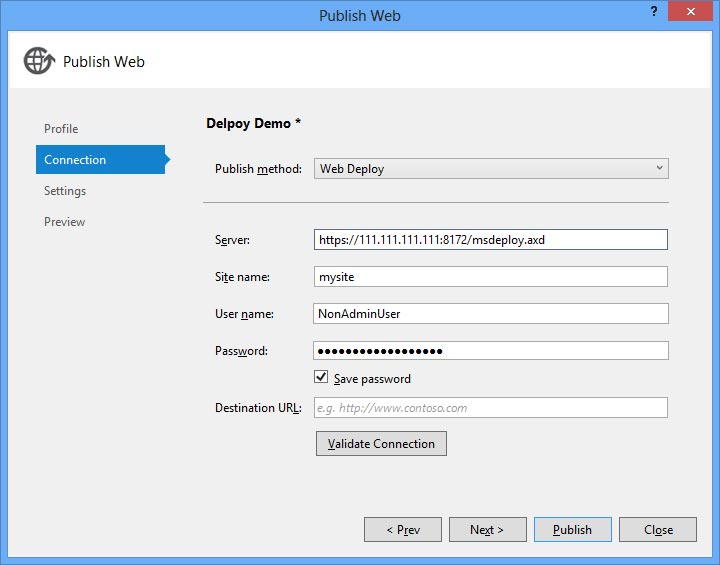
Настройка публикации Web Deploy в Visual Studio
После успешной настройки на стороне сервера необходимо настроить публикацию в Visual Studio. Для этого создаем профиль публикации, в методе публикации выбираем Web Deploy.
На следующем шаге выбираем конфигурацию Release. Здесь же можно указать строку подключения, на которую заменит VS при публикации (не пробовал). Получится удобная публикация решения в 1 клик:
Важно: название сайта должно быть таким же как оно отображается в IIS Management.
Важно: Если вы установили подписанный сертификат SSL на удаленном сервере, убедитесь, что вы установите флажок “Разрешить ненадежный сертификат” флажок. По умолчанию Web Deploy установит сертификат для вас, чтобы он был уникальный, однако он будет самоподписанный.
Также есть настройка, которая позволяет уточнить «Оставлять ли лишние файлы или нет». Веб деплой будет копировать только изменившиеся файлы с момента последней публикации.
Use the Web Deployment Tool
Introduction
The MicrosoftВ® Web Deployment Tool simplifies the migration, management, and deployment of Internet Information Services (IIS) Web servers, Web applications, and Web sites. Administrators can use command-line scripting with the Web Deployment Tool to synchronize IIS 6.0 and IIS 7 and above servers or to migrate an IIS 6.0 server to IIS 7 or above. The Web Deployment Tool also makes it possible for administrators and delegated users to use IIS Manager to deploy MicrosoftВ® ASP.NET and PHP applications to an IIS 7 and above servers.
With the Web Deployment Tool, you can:
Download and Install the Web Deployment Tool
The Web Deployment Tool is a managed code framework that includes the public application programming interfaces (APIs) and underlying engine. (This is the top-level node and cannot be removed.)
Choose Installation Options
Before you install the Web Deployment Tool, decide whether you want to use the remote service to perform live operations between two servers or if you prefer to use the offline mode.
Note that you only need the remote service installed on either the source or the destination. For example, to «push» all content from a server to a client, you can install the remote service on all client computers so that the content can be pushed from the source. Alternatively, you could have each client «pull» from the server and only install the remote service on the source.
To install the tool using the default remote service URL
Run the WindowsВ®Installer file to install the tool.
Select a Custom installation.
Click on the remote service node to install the remote service.
Complete the installation.
Manually start the service by running the following command:
Ensure that port 80 is open in the firewall.
To install the tool with a custom remote service URL
Open an administrative command prompt on Windows ServerВ® 2008, or a command prompt on Windows ServerВ® 2003.
Go to the directory where the setup file is located.
Run the following command (customize the port and URL specifications):
Manually start the service by running the following command:
Ensure that the port you have chosen is open in the firewall.
The tool will be installed to %programfiles%\IIS\Microsoft Web Deploy. This cannot be changed.
Starting the remote service after installation
The remote service listens on http://+/msdeployagentservice/ by default or at the URL that you specified if you performed a custom installation.
You should now start the remote service. You can do this by going to Start > Run, and then typing services.msc. The service is listed as the Microsoft Web Deployment Agent Service.
The service startup is Manual by default; you can set the startup to Automatic in Services.msc. You can also use the command-line tool Sc.exe, to set the startup to Automatic.
A Knowledge Base article provides more information about Sc.exe.
Use the Web Deployment Tool for Web Farms
The Web Deployment Tool can be used to deploy new applications to a Web farm or to keep changes synchronized between the Web farm servers. The Web Deployment Tool does not currently support a central UI or configuration store for a list of servers in a farm (for example, syncing multiple machines at once), but you can simply store this list of servers and perform synchronization operations against each server. These synchronization operations can easily be scheduled using MicrosoftВ® System Center or another scheduling mechanism. Resources that can be synchronized include Web sites or applications, content folders and files, databases, registry keys, and assemblies in the GAC, among others. You can also build custom «providers» that understand other types of resources that are not supported. For more information, see Using the Web Deployment Tool for Web Farms.
Package and Deploy Applications with the Web Deployment Tool
For information about packaging and deploying applications with the Web Deployment Tool, see the following articles.
Migrate from IIS 6.0 to IIS 7 or Above
You can use the Web deployment Tool to migrate:
Synchronize Web Servers
You can use the Web Deployment Tool to synchronize a Web site from a source to a destination on IIS 6.0, or IIS 7 or above. You can do this by «pushing» data to a remote destination or by «pulling» data from a remote source. You can also use a package (compressed file) to avoid installing the remote service. For more information, see the following articles:
Features of the Web Deployment Tool
The following information is an extensive list of the features of the Web Deployment Tool:
Seamless integration with IIS Manager and Visual Studio 2010 interface for creating packages and deploying them onto a machine, both locally and remotely.
Seamless integration with the Web Platform Installer to install community Web applications simply and easily.
Web application packaging:
Web application deployment:
Web server migration and synchronization:
In addition to using IIS Manager and Visual Studio 10, tasks can be performed using the command-line, Windows PowerShellв„ў cmdlets, or public APIs.
This article is based on material from: » Installing the Web Deployment Tool» by Faith Allington, published on September 1, 2009.
Microsoft Web Deploy v3 Readme
Overview
The Web Deploy is a tool for simplifying migration, management and deployment of Web applications, sites and servers. It can be used to package a Web site, automatically including content, configuration, certificates and databases. It can be used to synchronize between IIS 6.0, IIS 7.x and IIS8.0, or to migrate from IIS 6.0, IIS7.x to IIS 7.x and above. The packages created can be used for versioning, backup or deployment.
Features
The Web Deploy includes these key features:
Package Web sites and applications: Developers or administrators can package the configuration and content of installed Web applications, including SQL databases, and use the packages for storage or redeployment. These packages can then be deployed using the IIS Manager interface without requiring administrative privileges on a remote server.
Delegate deployment tasks to non-admins. Server administrators can choose to delegate deployment tasks to users who are not administrators. For example, in both shared hosting and enterprise environments, deploying content and marking a folder as an application can be delegated. More advanced tasks suitable to a dedicated environment, such as allowing a certificate, Web site or GAC’d assembly to be deployed, can also be enabled.
Simplify deployment for administrators. Server administrators will find the delegation useful, since deploying a Web application including a GAC’d assembly, certificate and application pool can be time-consuming even with all the permissions required.
Migration from IIS 6.0 and IIS7: The migrate operation provides administrators with a way to migrate sites or entire servers from IIS 6.0 to IIS 7 and above, IIS7 to IIS8 including their settings and content. A migration is essentially a way of synchronizing, filtered by migration rules.
Synchronization of IIS 6.0 / IIS 7/IIS8.0 The sync operation provides administrators with a way to quickly synchronize a site or server and deploy changes to existing sites and servers. A synchronization allows you to synchronize one source with one destination. For example, you can synchronize two directory paths or two web servers. The sync can be performed with local or remote objects.
Snapshot IIS 7.0 and above The snapshot, or archive, functionality allows administrators or developers to quickly take an archive of their web site or server for rollback, restore or backup purposes. Automatic snapshot feature also allows web site administrators to self-service some of above tasks.
Analysis of Dependencies on IIS 6.0 and above The analyze operation allows administrators to check what components are installed on the source server. In this way, they can determine if features are present that they will need in IIS 7.0 or that require more advanced setup than simply copying files.
Differential Synchronization. The tool will only synchronize what has changed between the source and the destination.
Easy Scripting through PowerShell: Common Web Deploy tasks can be automated using PowerShell cmdlets.
Installation Notes
Requirements
The following prerequisites must be fulfilled in order to install the tool:
Downloading and Installing
There are two separate downloadable packages for the tool; you will need to download the appropriate package. You can download the x86 or x64 versions.
Important Issues Fixed in this release:
Change: In previous versions of Web Deploy the tempAgent service would always run on port 80. In Web Deploy v3 RC this port can by changed by specifying the new port in the computername argument using the format computername=serverName:####, tempagent=true (where #### is the port number to use)
Change: Web Deploy V3 Automatically disables proxy settings. This was previously an issue for some clients, who were required to open Internet Explorer and disable proxy settings there prior to starting a sync.
Change: Added support for IPv6-style bindings in certificate sync logic. Previous versions could not sync IPv6 bindings properly.
Change: When syncing a child registry key to a server where the parent registry key does not exist, the parent registry keys up to the child key will now be created (without values) rather than the sync failing. For example, if syncing the registry key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\MySoft\TestWeb1 where the MySoft key does not exist on the destination machine, the MySoft key will be created on the destination machine allowing the sync will succeed.
Change: In some cases Web Deploy publishing removed inherited permissions on root folder of site. Web Deploy V3 fixes this issue.
Known Issues
Issue: Web Deploy v3 upgrade breaks SQLite syncs which were working using Web Deploy v2
Workaround:
Issue: Web Deploy Agent service does not work with local users accounts that are not the Administrator user account, but are members of the Administrators group. ERROR_USER_NOT_ADMIN error is returned.
The Remote Agent Service accepts either built-in Administrator or Domain Administrator credentials , any other administrator credentials will not work and will cause this error.
Workaround:
Use built in administrator account or domain user account (part of admin group on the local machine).The Remote Agent Service accepts either built-in Administrator or Domain Administrator credentials. If you have a non-domain setup and want to use account other that built-in administrator, please do following:
Issue: Some Management Service delegation rules do not work after Web Deploy is upgraded to Web Deploy 3.0
В· If your delegation rules have already been overwritten, re-create the affected rules manually.
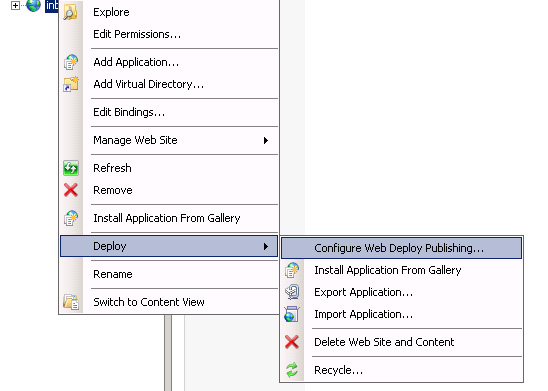
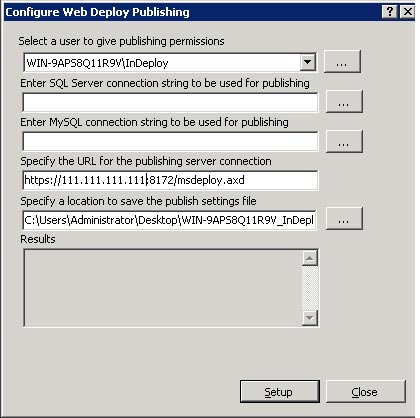
Issue: Cannot publish to site created with SetupSiteForPublish.ps1 PowerShell script or configured for Web Deploy publishing through the «Configure for Web Deploy Publishing. » UI
The site creation script as well as the UI to configure Web Deploy for an existing site sets the publishing URL to https://myserver:8172/msdeploy.axd. This computername is generally reachable within a network. However, it is often not reachable from outside the network, so it should be replaced with a public DNS name.
Workarounds:
Issue: Package created with Web Deploy V3 Does not work with WebDeploy V2. It results in System.NullReferenceException.
Workarounds:
Issue: Web Deploy UI in IIS Manager gives a «Unable to cast object of type» error
If the destination computer has Web Deploy v1.1 installed and the source computer has v2 installed, you may see this error. This is a cross-version incompatibility.
Workarounds:
Issue: If you are syncing an IIS 6.0 machine with lots of sites (causing the metabase to be over 500MB), then the tool may hang and stop responding.
Workaround:
Create a list of the sites and sync each site individually.
Issue: If you are syncing from a machine to a remote machine where the content or shared config is on a third, separate machine (i.e., UNC), then the remote agent will be unable to authenticate properly.
Workaround:
Either sync manually or use the Web Deployment Handler instead.
Issue: If you change shared configuration settings (such as enable or disable shared config), you will need to restart the remote agent afterwards.
Workaround:
Restart the agent after making a change to shared config.
Issue: If you are syncing a Web site where the path is %systemdrive%\wwwroot to a destination Web site where the system drive is different (C: instead of D:), then your Web site’s path will be expanded at the destination. This means if you have shared config means with different system drives and you rely on the %systemdrive% to ensure content works, you may break the site on a machine.
Workaround:
Add a replace rule to change the path during the sync.
Issue: If you try to package to an existing package file, this may not work correctly.
Workaround:
Use a new name or delete the old package file before creating a new package.
Issue: The Microsoft Web Deploy will not move the physical files for Script maps and items referenced in the Web Service Extension Restriction List, unless the files are located in a Web site’s content directories. This is because many ISAPIs may not migrate correctly, such as:
Workaround:
Manually include any script maps or files that do not require installation in a manifest file. See the Help for more information about creating manifest files.
Issue: Custom trust files referenced in the root level Web.config and Code Access Security (CAS) policy settings will not be moved.
Workaround:
Manually specify the custom trust file and the CAS policy file, security.config, in a manifest file. See the Help file for more information about creating manifest files.
Issue: If you move a site to a server that has a different trust level, you will not receive a warning.
Workaround:
Please ensure that the trust level is set correctly on the destination machine when doing a site level sync or migrate.
Issue: If you have a custom manifest file that is pointing to an invalid source, you may not receive an error.
Workaround:
If you are not seeing expected output when using a manifest file, try each item individually to see if they are mistyped or invalid.
Issue: FTP and SMTP are not included in the default definitions for webserver60.
Workaround:
Issue: Inherited properties are not migrated with an IIS 6.0 site migration. A common example is authentication set at the server level with all sites inheriting this property. When you migrate a single site, it will now inherit the settings of the new destination server. If the destination server settings are not the same, your site could break. This applies to every inherited property, including mime maps, script maps, etc.
Workaround:
Use the metadataGetInherited flag to copy inherited settings to the site level when you sync or migrate a web site on IIS 6.0. Or ensure the server settings are the same on source and destination servers or manually set the site to use correct settings.
Troubleshooting Installation Issues
If you encounter any problems during installation, you can run appropriate command listed below for your version of Windows to create a log file that will contain information about the installation process:
msiexec /L msdeployinstall.log /I
msiexec /L msdeployinstall.log /I
You can analyze this log file after a failed installation to help determine the cause of the failure.
For More Information
The following additional resources for the Web Deploy are available on IIS.net: