как удалить postgresql mac os
How to uninstall PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL is a powerful open source database system that leverages and extends the SQL language, combined with a host of features to securely store and scale the most complex data workloads. PostgreSQL has tons of various features designed to help developers build applications, administrators protect data integrity and create resilient environments, and help manage data regardless of dataset size.
PostgreSQL is not typically problematic, but if you are experiencing some issues with it, it is recommended to reinstall the application instead of trying to fix the problem. Thus, here we are going to explain how to uninstall PostgreSQL from a Mac computer easily and quickly.
This is a special uninstaller that will help you to completely uninstall any application from Mac along with their caches, logs, login items, preferences and browsers extensions.
How to remove PostgreSQL using Terminal
Deleting PostgreSQL just by dragging-and-dropping it into the Trash is not the correct way to uninstall apps. In this case, all the Postgre system service files will remain on your computer and keep cluttering up your disk space. Meaning, they will not let you correctly reinstall the app in the future.
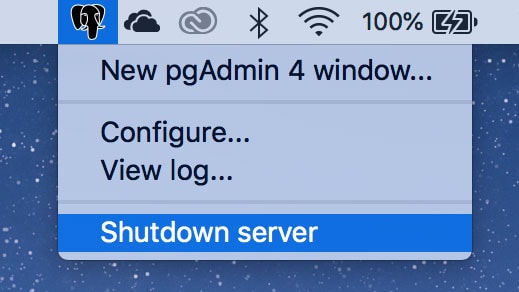
To manage the complete Postgre uninstallation first of all, you should stop the Postgres server on your Mac. For this, click on the Elephant icon in the toolbar and select Shutdown server
If you installed Postgres with its Installer, then you can use the Terminal command line to remove Postgres. For this, go to the Applications folder, open Utilities subfolder, and launch Terminal. After that run the uninstaller using the following command:
If you get the message that this file does not exist, then skip to the second PostgreSQL removal way. If the command runs the uninstaller, proceed to the next steps. 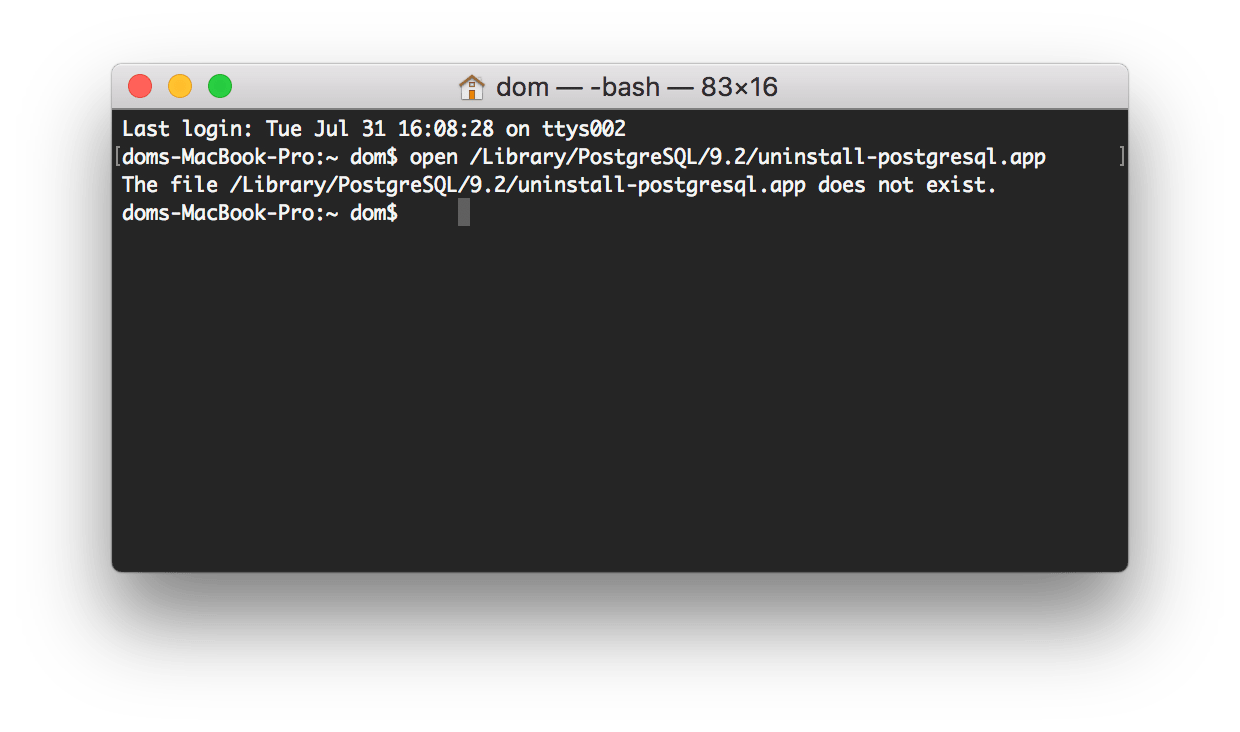
Enter the administrator password to launch the uninstaller. Then follow the provided steps to remove the PostgreSQL and data folders.
Unfortunately, the root uninstaller doesn’t delete all service files of the program, so you will need to remove them manually. For this, use the commands below:
That’s all with the first method of removal. If for some reason this method does not work for you or you simply do not want to waste your time we recommend to uninstall PostgreSQL with the App Cleaner & Uninstaller tool, which will automatically find all support files of PostgreSQL and remove the application entirely. Keep reading this article to find out more about this tool.
The easiest way to remove PostgreSQL from Mac
Uninstalling PostgreSQL with Terminal may be a really time-consuming process. Moreover, you might have missed some service files and left them on your Mac’s hard drive. That’s why we recommend that you uninstall PostgreSQL automatically.
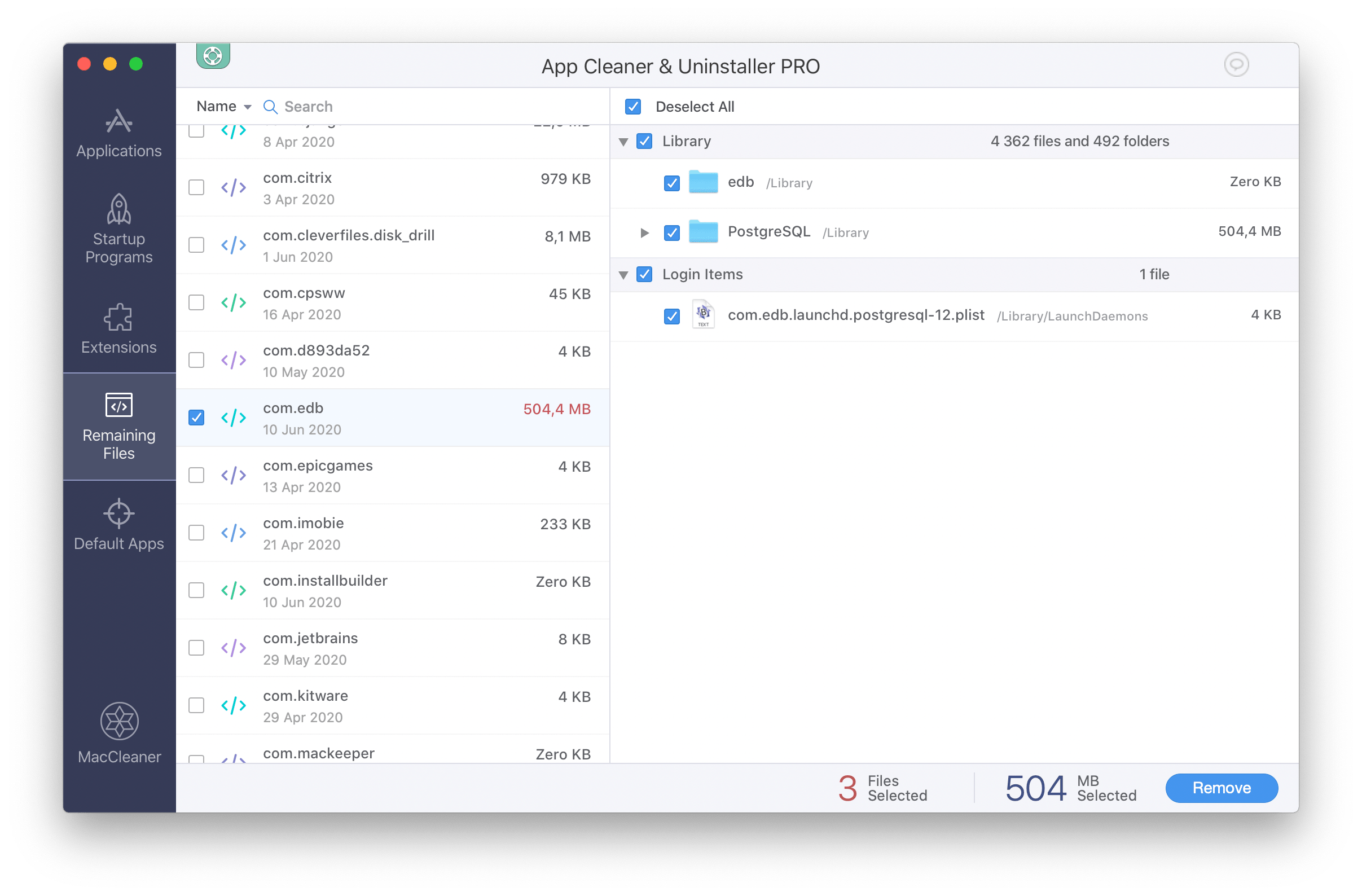
For the automatic uninstallation method, you need to use a special free cleanup application – App Cleaner & Uninstaller. This software automatically gathers all the service files of each app and allows you to uninstall them with one click. With this uninstaller, you can uninstall PostgreSQL without any extra steps and it will not take much of your time. Here are a few steps to do that:
Note that App Cleaner & Uninstaller automatically detects all the support files of the apps, so you don’t need to waste your time searching and removing them manually. That is why if you have already deleted PostgreSQL in a regular way, just by dragging-and-dropping it into the Trash, we recommend you to switch to the Remaining Files tab. That section will display all the leftovers of previously incorrectly deleted applications. So that is the perfect option to quickly get some free space.
Conclusion
In this article, we provided you with two ways of uninstalling PostgreSQL from Mac. You can uninstall it manually using the Terminal, which is a time-consuming task or you can follow the instruction of automatic uninstallation. Nektony recommends using a professional App Cleaner & Uninstaller tool. This application was developed specially for fast, safe, and complete uninstallation of any no longer needed application.
App Cleaner & Uninstaller
Uninstall any Mac application in 2 minutes.
How To Completely Uninstall PostgreSQL
Introduction
If you’re using PostgreSQL, you may need to remove the package from your system at some point. It’s important to know how to uninstall PostgreSQL properly to make sure all components of the package are completely removed and you don’t encounter any errors. In this article, we’ll explain how to uninstall PostgreSQL from Linux, macOS and Windows operating systems.
NOTE: Be sure to elevate the privileges for any of the commands in this article with sudo if the terminal returns a Permission denied error.
Uninstall and remove PostgreSQL on Debian Linux
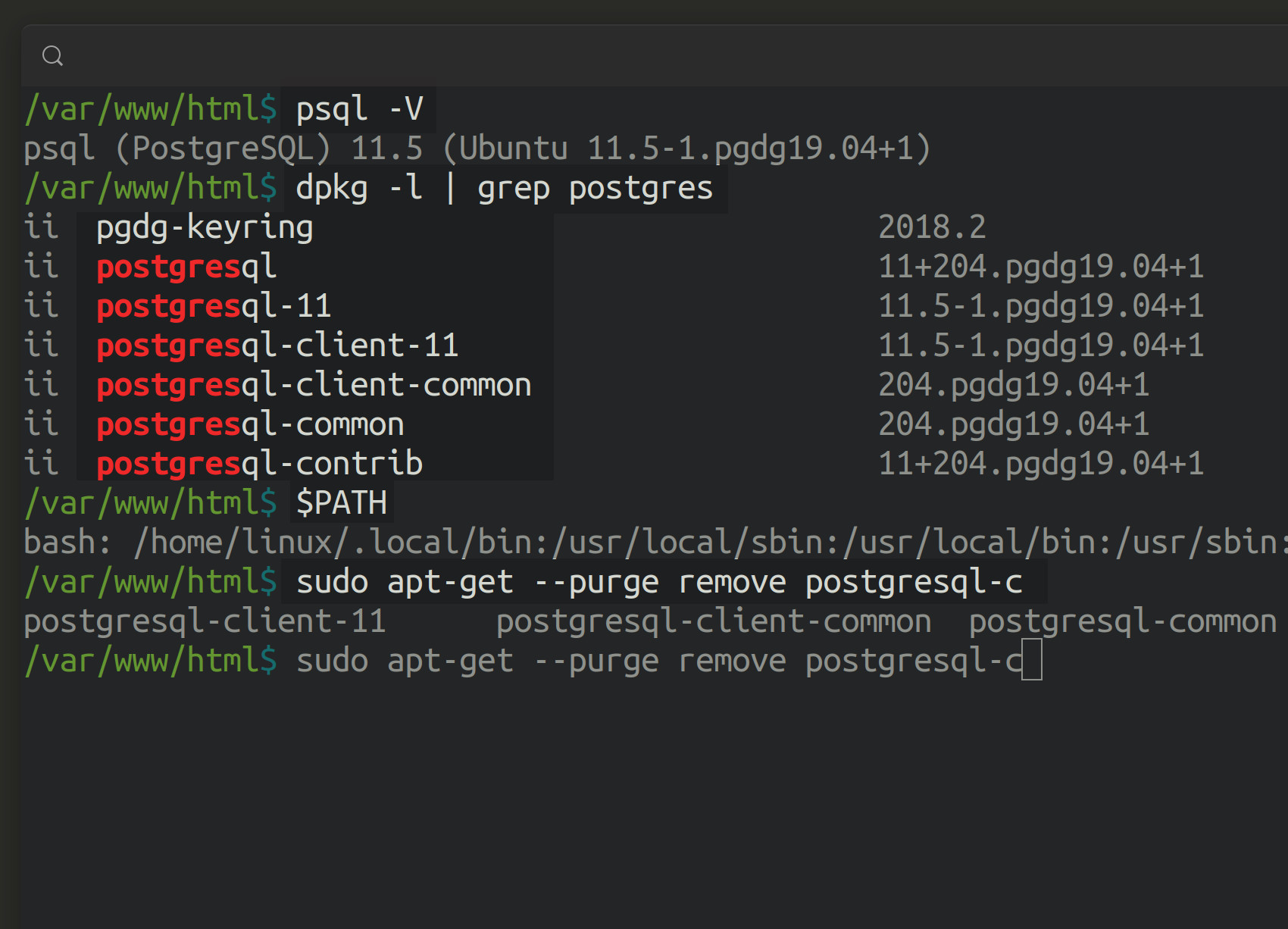
You can use the apt-get command to completely remove PostgreSQL on a Debian-based distribution of Linux such as Linux Mint or Ubuntu:
Grep for all PostgreSQL packages in Debian Linux
Remove all of the PostgreSQL data and directories
Uninstall and remove PostgreSQL packages on Fedora Linux
You can use the YUM repository’s yum command to uninstall PostgreSQL on Fedora-based distributions of Linux such Red Hat or CentOS:
Be sure to remove the pgsql directory as well:
NOTE: Keep in mind that sudo is not enabled for RHEL users by default. Instead, use the su (switch user) command to enter as root and execute the above commands with elevated privileges if necessary.
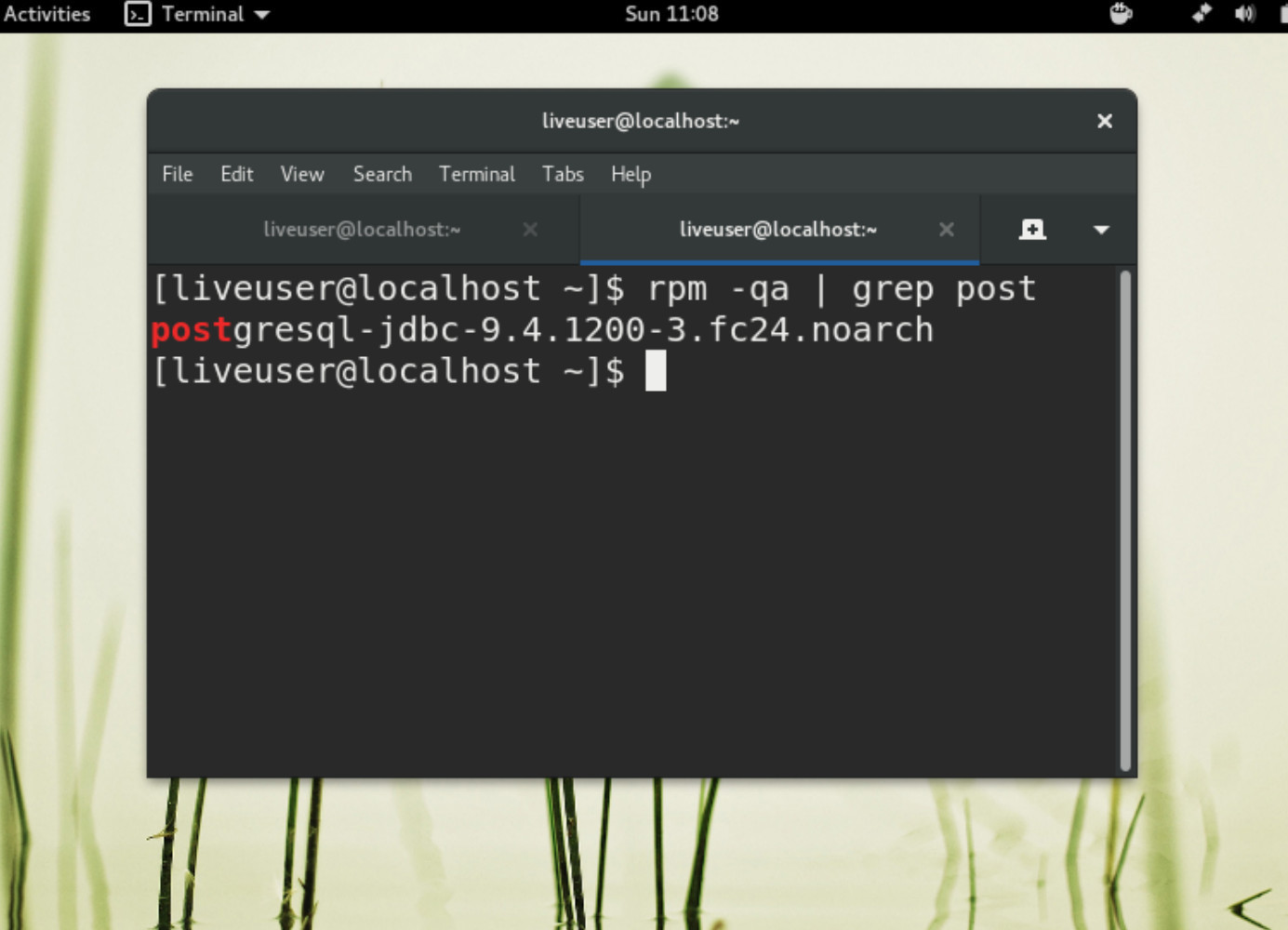
Grep for the PostgreSQL packages in Fedora using ‘rpm’
If you prefer, you can shorten the search to something like post as well:
You can also use grep in conjunction with YUM’s list command to return a list of all package instances of PostgreSQL:
Uninstall the PostgreSQL package using YUM remove
Once you’ve located the package, use YUM’s remove command to uninstall PostgreSQL from your Linux system:
Navigate to the assigned directory for the PostgreSQL data, and then use the rm command to delete all of your databases and tables.
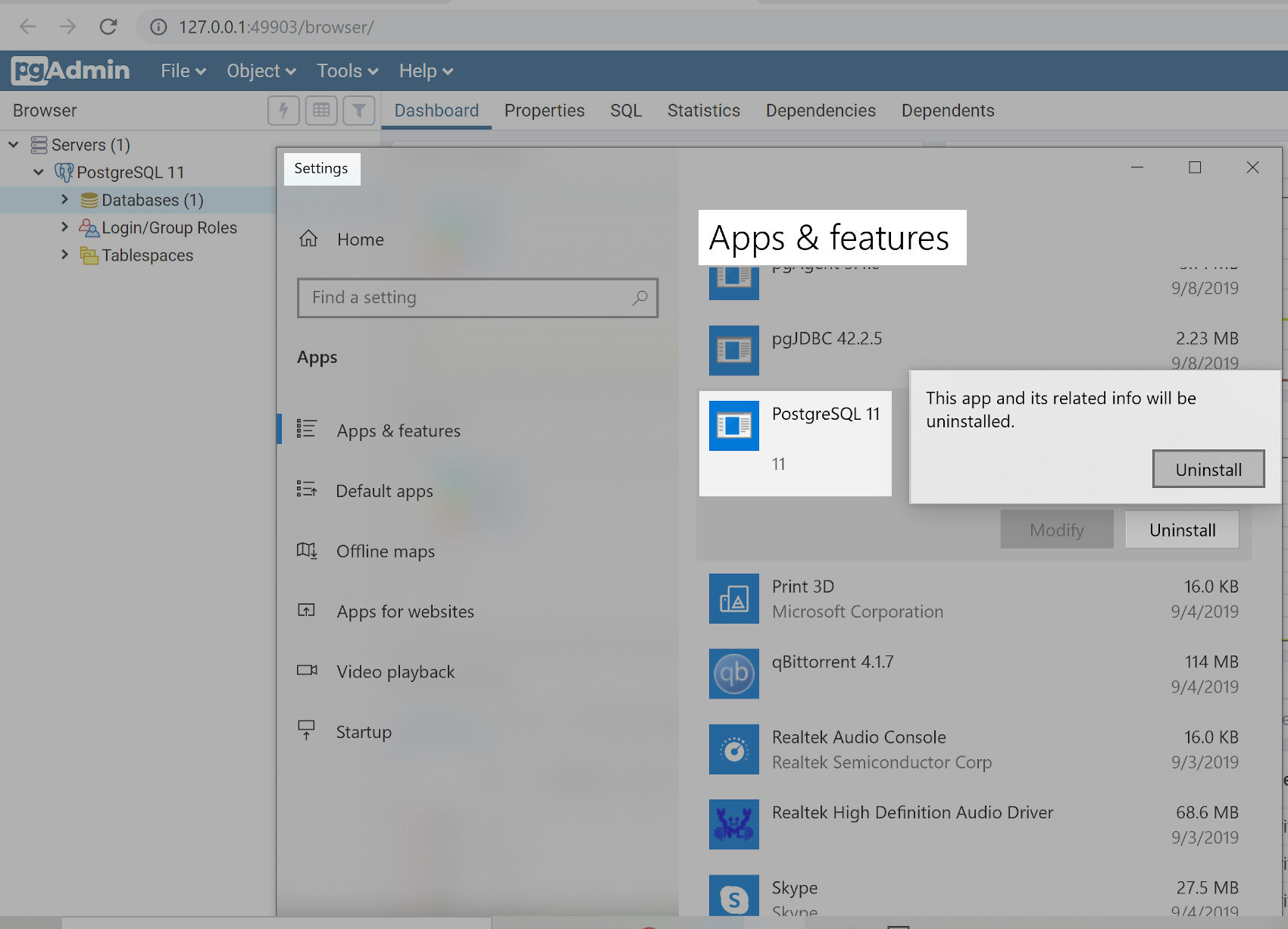
Uninstall and remove PostgreSQL from Windows
If you’re using Windows, type uninstall or remove into the search bar at the bottom left-hand side of the screen:
Then, follow the steps for the removal process, making sure to select the “Entire Components option when prompted.
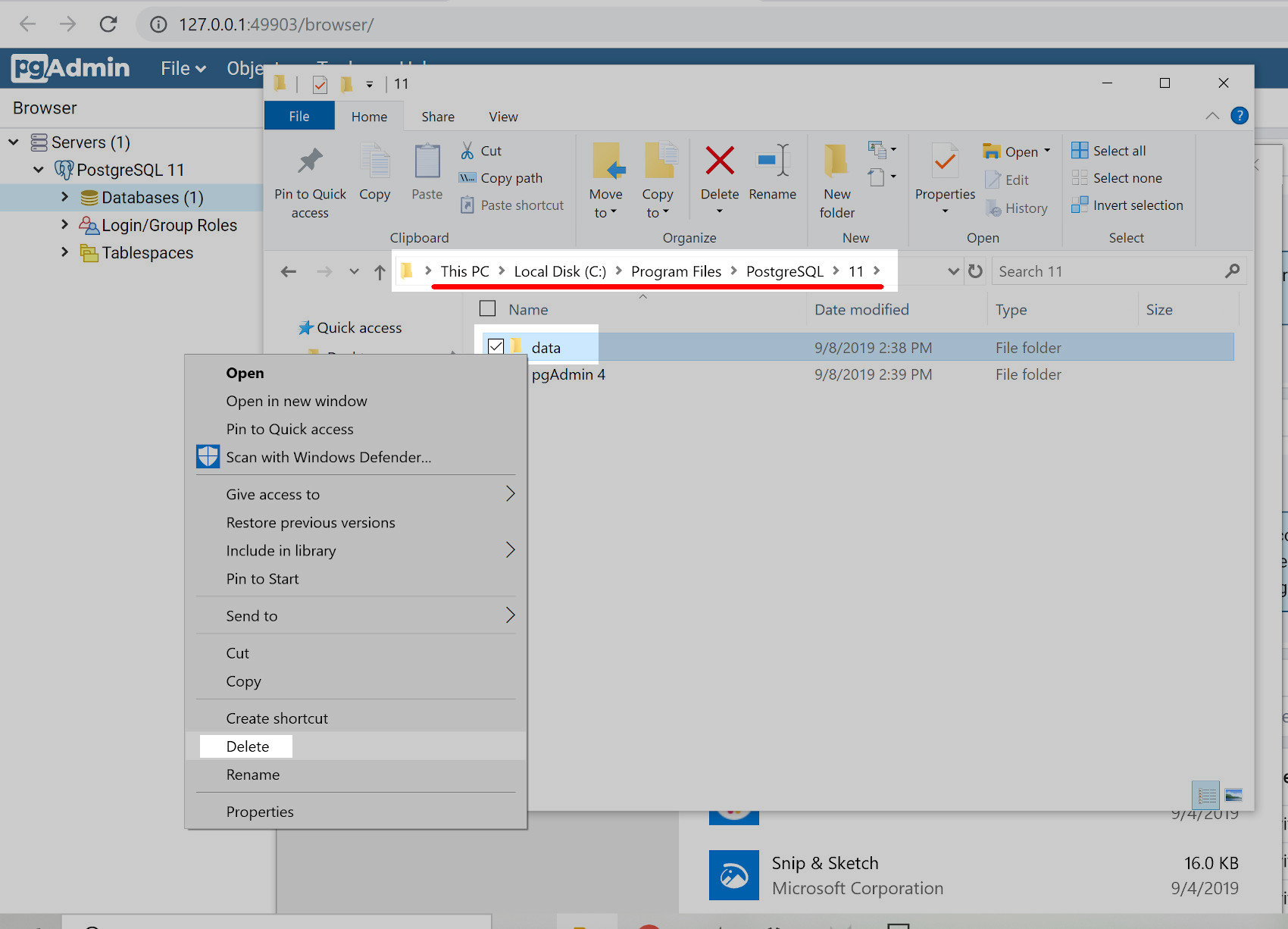
Delete the data folder for PostgreSQL in Windows
After you’ve completed the removal process described in the previous section, open File Explorer for Windows and navigate to the data folder. Right-click the data folder and click the Delete button. Be sure to empty the recycle bin afterwards to ensure that any sensitive data has been properly deleted.
After all of the data has been deleted, you should restart Windows 10.
Uninstall and remove PostgreSQL on macOS
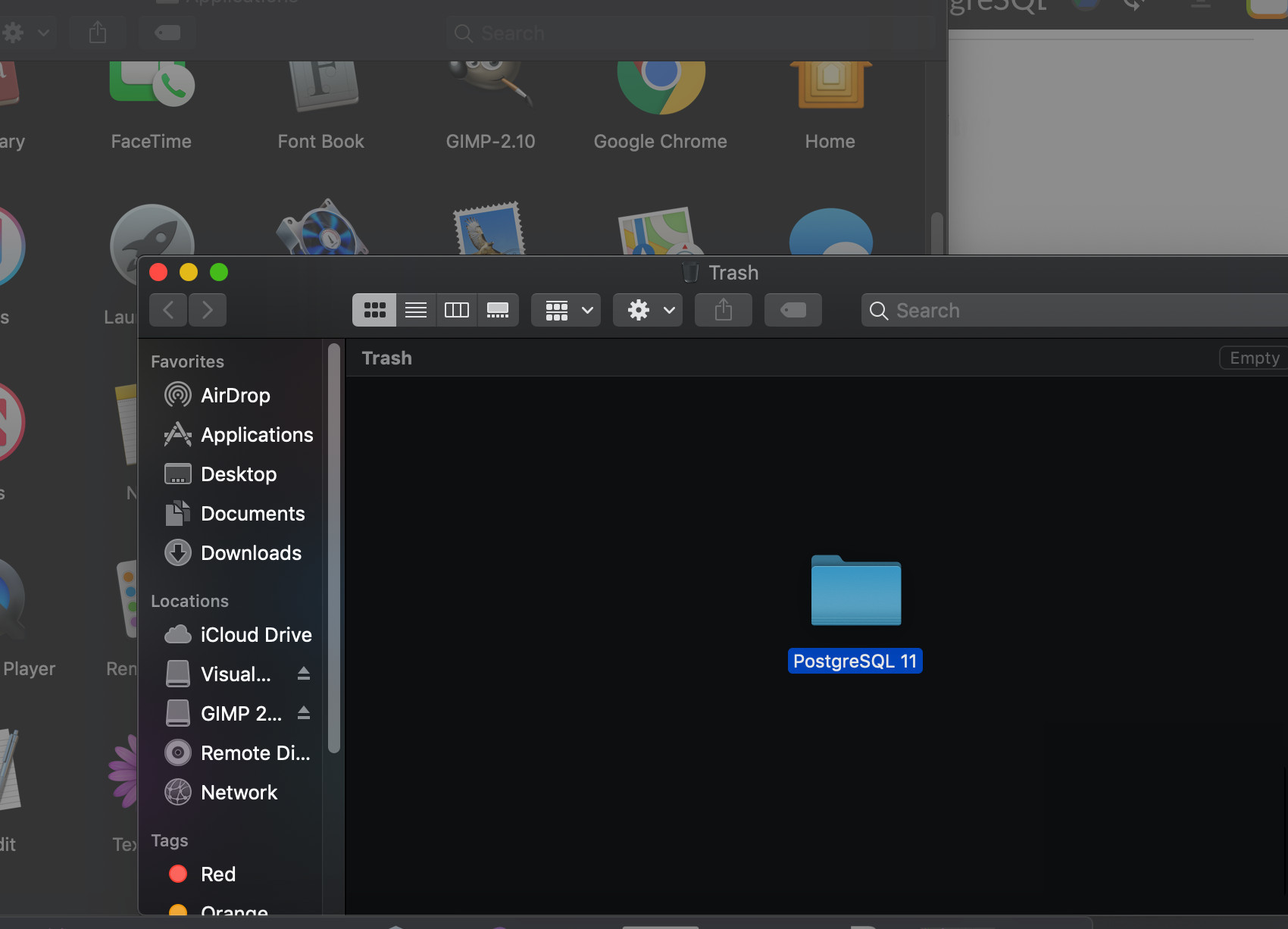
To uninstall PostgreSQL on macOS, open a new instance of Finder and navigate to the Applications directory. Look for the PostgreSQL folder and drag its contents to the Trash application folder in macOS.
Remove the PostgreSQL data in a terminal in macOS
After you’ve removed the PostgreSQL folder, open the Utilities folder in a Finder window, and then open the Terminal application.
Use the cd command to navigate to the PostgreSQL directory. You can do this by typing the directory path into the terminal prompt and pressing Return:
Don’t forget to empty the Trash application’s contents when you are finished.
Uninstall the Homebrew installation of PostgreSQL on macOS
You can use the brew command in a macOS terminal window to remove the Homebrew version of PostgreSQL. First, use the list command to return all of the applications installed using Homebrew:
Then, use the following command to force the removal the Homebrew installation of postgresql :
Conclusion
If you find yourself needing to uninstall PostgreSQL, it’s important to do a careful and thorough job. Taking shortcuts when it comes to the removal process can leave sensitive data remaining on your machine. In this article, we explained how to uninstall and remove PostgreSQL from Windows, Linux and macOS. With the step-by-step instructions detailed in this tutorial, you’ll be ready to remove PostgreSQL from any of your own machines.
Pilot the ObjectRocket Platform Free!
Try Fully-Managed CockroachDB, Elasticsearch, MongoDB, PostgreSQL (Beta) or Redis.
Как я могу полностью удалить Postgres со своего Mac?
Я не использовал MacPorts, Fink или другие инсталляторы Unix, кроме Homebrew, в жизни этого Mac. Homebrew отказывается от права собственности на установку Postgres:
Поэтому, несмотря на то, что я установлен, у меня сломана установка Postgres, которую я хотел бы полностью стереть
Как я могу полностью стереть Postgres из моей системы, чтобы я мог установить его с помощью установщика и получить одну установку Postgres вместо жутких полутора установок?
2 ответа 2
Похоже, вы только что удалили несколько файлов в Finder.
Предполагая, что вы использовали установщик отсюда, вы должны следовать инструкциям в руководстве по удалению:
Пробные
Если вам нужно удалить PostgreSQL, вы можете в любое время запустить деинсталлятор, созданный в процессе установки. Обратите внимание, что деинсталлятор никогда не удалит ваш каталог данных или учетную запись пользователя службы. Вы можете найти деинсталлятор в установочном каталоге и запустить его так же, как вы запустили инсталлятор. Обычно параметры командной строки не требуются. В Windows вы также можете запустить деинсталлятор из панели управления «Установка и удаление программ».
Другими словами, просто запустите деинсталлятор, установленный вместе с остальной частью программы.
После запуска любых деинсталляторов, следующее должно помочь вам найти любые оставшиеся файлы конфигурации или конфигурации SQL в вашем каталоге Library (общий источник странного поведения переустановки)
Если там есть что-то, что выглядит как часть установки PostgreSQL, удаление их перед переустановкой может помочь. Иногда там скрытые папки скрыты глубже.
How to Uninstall/Reinstall PostgreSQL (Mac)
Other Guides
Table of Contents
This guide is for the rare situations when using Apple’s OS X when you need to completely reinstall the PostgreSQL Server when advised by PokerTracker technical support. Following these instructions will delete all databases from your computer, we advise that you backup your databases prior to performing a total reinstall. These instructions require you to type command line instructions within the OS X Terminal, you will usually find the Terminal inside the /Applications/Utilities.
To verify which version of PostgreSQL you will be replacing, at the Terminal command line prompt type:
The Terminal will respond with a list of all the directories shown in the folder found at /Library/PostgreSQL, each version number will be installed in it’s own directory. In the example shown below we can confirm that PostgreSQL 9.0 is installed.
The examples used in this Guide assumes that PostgreSQL version 8.4 is installed, in the event you have a different version of PostgreSQL installed then replace the version number accordingly. For example, if you need to uninstall PostgreSQL 9.0 then replace /Library/PostgreSQL/8.4/ with /Library/PostgreSQL/9.0/
1) Execute (double click) /Library/PostgreSQL/8.4/ uninstall-postgresql which will uninstall the PostgreSQL installation.
2) Stop the server.
sudo /sbin/SystemStarter stop postgresql-8.4
3) Remove menu shortcuts:
4) Remove the ini file
sudo rm /etc/postgres-reg.ini
5) Removing Startup Items
sudo rm /Library/StartupItems/ postgresql-8.4
6) Remove the data and installed files (all databases will be lost at this point)
7) Delete the user postgres
8) Reboot your computer
9) Reinstall PokerTracker 4 and PostgreSQL using the PokerTracker 4 installer, or manually install the latest version of PostgreSQL found at http://postgresql.org
If you have any issues, please contact PokerTracker support for assistance.
How to Uninstall PostgreSQL with Homebrew (macOS)
Learn how to completely uninstall (and reinstall) PostgreSQL with Homebrew on Mac.
If you’re having problems starting up your PostgreSQL databases running on Homebrew, such as the classic:
You can try restarting PostgreSQL services:
But that often doesn’t work.
Sometimes the fastest way to solve the problem by uninstalling PostgreSQL entirely, and reinstalling a fresh version.
Uninstall PostgreSQL with Homebrew
This will show you how to completely remove PostgreSQL with Homebrew.
Warning: If you have any important projects on your machine that run on PostgreSQL databases, now is the time to back them up, because the following will wipe out PostgreSQL completely!
First Open your Terminal, and run the following command to make sure that PostgreSQL is actually installed with Homebrew:
If it doesn’t show up, you’re in the wrong tutorial!
Before you move on, run the following two commands to make sure that your Homebrew installation is healthy, and up to date:
brew doctor is Homebrew’s self-diagnosis tool.
Now uninstall PostgreSQL with Homebrew with this command:
When the uninstaller is finished, remove all your local PostgreSQL files with these two commands:
PostgreSQL is now completely gone from your machine.
Install PostgreSQL with Homebrew
If you want to reinstall PostgreSQL with Homebrew again, run another update on Homebrew (for good measure):
I know you just updated Homebrew, but sometimes I have to do it twice to make it work (I don’t know why).
And then install PostgreSQL:
Now you can start PostgreSQL services with this command:
To test that it works, we can create the default database:
Connect to PostgreSQL by running this command:
If everything went well your terminal will output the following (or similar):
Has this been helpful to you?
You can support my work by sharing this article with others, or perhaps buy me a cup of coffee 😊