как установить yarn на windows
How to Install Yarn on Windows
What is a Package Manager?
Package Manager is a tool that installs, updates and manages the software packages you need. With the help of such tools, you can always have the latest version of the libraries you need with your software. You can also think only of developing the core of your software without having to search for packages and their peripherals.
Note: Node.js must be installed before installing Yarn.
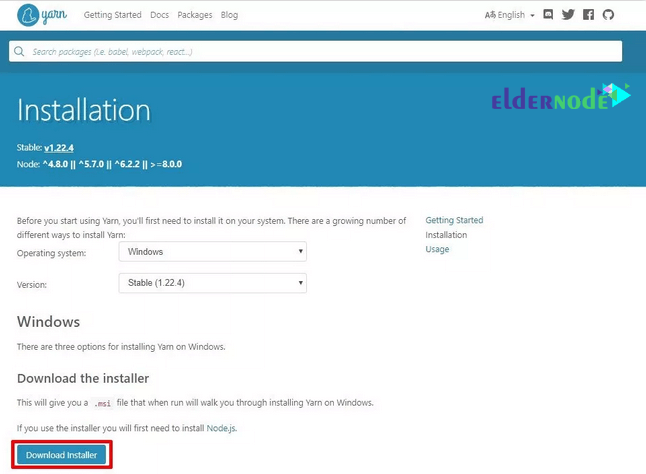
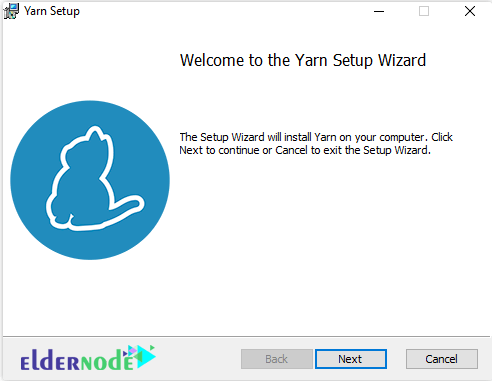
MSI Installation
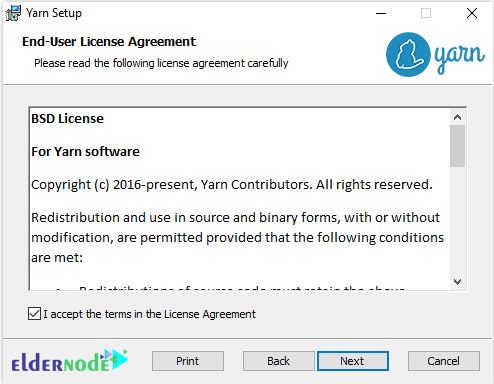
accept the license agreement.
And finally, click on the Finish button.
Now, you can verify Yarn was installed using the following CLI commands :
Chocolatey Installation
Another way to install Yarn is by using the Chocolatey package manager for Windows. This method is convenient because Chocolatey will determine whether node.js is already installed and if not, it will automatically install it for us. It is important to do everything as an administrator.
Once Chocolatey is set up, you can install Yarn using the following command:
You can verify your installation of yarn using the following command:
Scoop Installation
The third method of installing Yarn is by using the Scoop command line installer for Windows.
Scoop has functionality that is similar to Chocolatey, but the main difference being that Chocolatey will install node.js if we do not already have it installed but scoop will not.
Scoop can be installed using the information found at the scoop website. To install node.js using scoop, run the following command:
The best method to review many of the Yarn commands is to run the help command:
Start a New Project
Installing Dependencies
Use one of the two following commands, to install all the dependencies for a project:
To add a dependency to a project, use one of the following command formats:
1) dev Dependencies
2) peer Dependencies
3) optional Dependencies
Upgrade Yarn
To upgrade Yarn to the latest version, run one of the following commands:
Also, see:
Dear user, we hope you would enjoy this tutorial, you can ask questions about this training in the comments section, or to solve other problems in the field of Eldernode training, refer to the Ask page section and raise your problem in it as soon as possible. Make time for other users and experts to answer your questions.
How to Install Yarn on Windows
What is Yarn?
Prerequisites
Node.js must be installed before installing Yarn. We can verify if node.js is installed on our system using the Windows terminal or powershell.В
1. Open the terminal by pressing the Win+R buttons and then enter cmd.В
2. Using the command line, we can verify if Node.js is installed with the command:
If we do not have node.js installed, we can go to the main node.js website and download the installer.
Next, we need to run the installer.
Now, we should accept the license agreement.
Now, leave all the defaults set and click Next to install node.js.
Finally, click on Finish, to complete the installation. Now we can rerun our command to verify node.js installed correctly using the following command in the terminal:
Yarn Installation
MSI Installation
Now, accept the license agreement.
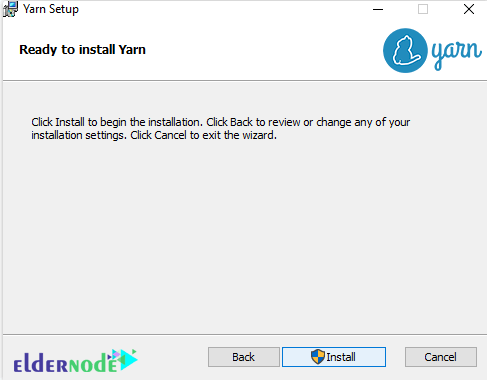
Then, click Install.
And finally, click on the Finish button.
Now, we can verify Yarn was installed using the following CLI commands.
Chocolatey Installation
Another way to install Yarn is by using the Chocolatey package manager for Windows. This method is convenient because Chocolatey will determine whether node.js is already installed and if not, it will automatically install it for us. It is important to do everything as an administrator. Here are the instructions for installing Chocolatey.
Once Chocolatey is set up, we can install Yarn using the following command.
Finally, we can verify our installation of yarn using the following command.
Scoop Installation
The third method of installing Yarn is by using the Scoop command line installer for Windows. Scoop has functionality that is similar to Chocolatey, but the main difference being that Chocolatey will install node.js if we do not already have it installed but scoop will not. Scoop can be installed using the information found at the scoop website.В
To install node.js using scoop, run the following command.В
Next, we can install yarn using this command.
Migrating from Yarn 1
We’ve been compiling helpful advice when porting over from Yarn 1 on the following Migration Guide. Give it a look and contribute to it if you see things that aren’t covered yet! Make sure to consult the PnP Compatibility Table and enable the node-modules plugin if required!
About global installs
For this reason, Yarn 2 and later are meant to be managed on a by-project basis. Don’t worry, little will change! Just make sure to first install the global Yarn binary that we will use to spawn the local ones:
You’ve probably remarked the global Yarn is from the «Classic» line (1.x). This is expected! One extra perk of this system is that projects configured for Yarn 1 will keep using it instead of suddenly having to migrate to the 2.x configuration format. We wouldn’t have had to do this if Yarn had been «project locked» from the beginning, but hindsight is 20/20 😉
«Berry» is the codename for all versions of Yarn from 2 onwards: 2.x, 3.x, etc. It’s also the name of our repository!
Updating to the latest versions
Should you later want to update Yarn to the latest version, just run:
Yarn will then download the most recent binary from our website, and install it in your projects. Don’t forget to run a new install to update your artifacts, and to commit the results!
Installing the latest build fresh from master
From time to time even the most recent releases aren’t enough, and you then will want to try out the very latest master to check if a bug has been fixed. This has become very simple with Yarn 2! Just run the following command:
Yarn 2 — Устанавливаем и разбираемся
Знакомство
Yarn 2 (Berry) — это новый выпуск революционного и хорошо зарекомендовавшего себя менеджера пакетов Yarn, включающий в себя такие особенности, как: Plug’n’Play, возможность расширения модульного API, оффлайн-кэш и улучшенную поддержку рабочих пространств.
Plug’n’Play
В новой документации Yarn подробно рассказывается о недостатках node_modules, как структуры папок, и объясняется, почему необходим новый взгляд на управление зависимостями.
Монорепозитории
Не зависимо от того, являетесь бы поклонником монорепозиториев или нет, чтобы обеспечить качественное управление большими проектами и сложными рабочими процессами, потребуется хороший набор инструментов.
Популярным рецептом настойки JavaScript монорепозитория является комбинация рабочих пространств Yarn и использование Lerna в качестве менеджера проектов.
Хорошая новость заключается в том, что теперь Yarn может одновременно выполнять функции как менеджера пакетов, так и менеджера проектов, пытаясь обеспечить положительный опыт работы в этом аспекте.
Модульная архитектура, плагины
Сделав важный шаг вперед, Yarn 2 был переработан в пользу нового модульного API, расширяемого при помощью плагинов. В настоящее время большинство функций уже реализовано с их помощью — даже yarn add и yarn install являются предустановленными плагинами!
Как начать работу?
Установка
Yarn придерживается стратегии глобальной установки первой версии, а уже затем переключения на вторую для конкретного проекта.
Сначала установим глобальный Yarn, который мы будем использовать для создания локальных экземпляров:
“Berry” — кодовое имя релизной ветки Yarn 2.
Изменим версию Yarn конкретно для каталога my-app :
После выполнения данной команды установка будет завершена, и можно переходить к установке зависимостей!
Добавление зависимостей
Общие команды управления остались теми же, что и в предыдущих версиях:
yarn init — инициализация проекта
[—dev] — добавление пакета
Также, вы можете увидеть некоторые изменения консольного интерфейса в новой версии Yarn:
каждый набор связанных задач, выполняемых в процессе установки, сгруппирован;
почти все сообщения имеют собственные коды ошибок, которые можно найти в документации;
цвета теперь используются только для обозначения важных частей каждого сообщения.
Установка React.js с Yarn-плагином TypeScript
Далеко не все пакеты поставляются с собственными определениями типов, но уже нет поводов для волнения, ведь там, где их нет, Yarn возьмёт работу на себя.
Перед выполнением операцией ниже, следует установить Yarn Berry для рабочей директории и убрать детей от экрана.
Инициализируем package.json и установим плагин TypeScript:
Проведем установку библиотеки React:
Зависимости @types/ были успешно установлены!

Что в итоге
Ветка Yarn 1.x (Classic) уже официально перешла в статус поддержки, предполагающей только исправление уязвимостей.
Для React Native всё таки придётся подключать node modules.
Если Yarn не подружится с вашей IDE, нужно будет кое-что установить. Не скучайте!
Installation
Install via npm
It is recommended to install Yarn through the npm package manager, which comes bundled with Node.js when you install it on your system.
Once you have npm installed you can run the following both to install and upgrade Yarn:
Alternatives
Alpine
On Alpine Linux (3.6+), you can install Yarn with apk.
Currently, there are no Alpine packages available for RC or nightly builds of Yarn. Please use the tarball:
Installation Script
One of the easiest ways to install Yarn on macOS and generic Unix environments is via our shell script. You can install Yarn by running the following code in your terminal:
The installation process includes verifying a GPG signature. View the source on GitHub
You can also specify a version by running the following code in your terminal:
See the releases for possible versions.
Manual Install via tarball
You can install Yarn by downloading a tarball and extracting it anywhere.
Before extracting Yarn, it is recommended that you verify the tarball using GPG:
Path Setup
If Yarn is not found in your PATH, follow these steps to add it and allow it to be run from anywhere.
Arch Linux
On Arch Linux, Yarn can be installed through the official package manager.
Currently, there are no Arch packages available for RC or nightly builds of Yarn. Please use the tarball:
Installation Script
One of the easiest ways to install Yarn on macOS and generic Unix environments is via our shell script. You can install Yarn by running the following code in your terminal:
The installation process includes verifying a GPG signature. View the source on GitHub
You can also specify a version by running the following code in your terminal:
See the releases for possible versions.
Manual Install via tarball
You can install Yarn by downloading a tarball and extracting it anywhere.
Before extracting Yarn, it is recommended that you verify the tarball using GPG:
Path Setup
If Yarn is not found in your PATH, follow these steps to add it and allow it to be run from anywhere.
CentOS / Fedora / RHEL
On CentOS, Fedora and RHEL, you can install Yarn via our RPM package repository.
If you do not already have Node.js installed, you should also configure the NodeSource repository:
Then you can simply:
Currently, there are no RPM packages available for RC or nightly builds of Yarn. Please use the tarball:
Installation Script
One of the easiest ways to install Yarn on macOS and generic Unix environments is via our shell script. You can install Yarn by running the following code in your terminal:
The installation process includes verifying a GPG signature. View the source on GitHub
You can also specify a version by running the following code in your terminal:
See the releases for possible versions.
Manual Install via tarball
You can install Yarn by downloading a tarball and extracting it anywhere.
Before extracting Yarn, it is recommended that you verify the tarball using GPG:
Path Setup
If Yarn is not found in your PATH, follow these steps to add it and allow it to be run from anywhere.
Debian / Ubuntu
On Debian or Ubuntu Linux, you can install Yarn via our Debian package repository. You will first need to configure the repository:
On Ubuntu 16.04 or below and Debian Stable, you will also need to configure the NodeSource repository to get a new enough version of Node.js.
Then you can simply:
If using nvm you can avoid the node installation by doing:
Path Setup
If Yarn is not found in your PATH, follow these steps to add it and allow it to be run from anywhere.
Gentoo Linux
On Gentoo Linux, you can install Yarn with portage.
Currently, there are no Gentoo packages available for RC or nightly builds of Yarn. Please use the tarball:
Installation Script
One of the easiest ways to install Yarn on macOS and generic Unix environments is via our shell script. You can install Yarn by running the following code in your terminal: